Title of best practice
Integrated Comprehensive Rural Healthcare And Professional Health Education
The context that led to initiation of practice:
This Healthcare and Health Education Model is part of a "Pravara Model of Integrated Rural Development"conceived and launched by founder visionaries in a drought-prone rural part of Ahmednagar, Maharashtra to uplift rural communities in 1949.
Objective
A) To offerpreventative, curative, and rehabilitative services, quality medical care to rural
poor, vulnerable groups, at reasonable price
B) To provide primary healthcare services to rural areas through Rural Health and Training
Centre (RHTC), Urban Health Centres (UHC), Rural Health Centres (RHC), Mobile
Medical and Dental Clinics (MMDCs), Motorbike Ambulance-cum-clinics (MAC), Gram
Arogya Banks (GAB), School Health Hygiene and Environmental Program(SHAPE) &
Arogya Mitras.
C) To enhance healthcare services at MD Campsby deploying well-trained, qualifieddoctors &
referral services through Teaching Hospital
D) To build connections with GOs, NGOs, HEIs, and International collaborators to support
rural healthcare initiatives.
E) To conduct need based research on rural communities, prevention, treatment, care models
F) To actively involve public, local communities in development of healthcare and outreach.
1. The farmer-led cooperative movement, sparked by visionary founders, aimed to tackle
multifaceted rural issues leading to "Sweet Revolution".
2. Established in 1972, Pravara Medical Trust aims for an integrated healthcare, education,
and research, focusing on community service.
3. Various institutions established over years for quality health education, develop holistic
healthcare model. In 2003, merged into Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences (PIMS -
DU) approved by UGC, MHRD, GOI under regulations for deemed universities.
4. Development primarily focused on healthcare for women, children, elderly, and other
vulnerable sections of community
5. PIMS-DU collaborates with stakeholders for health disparities, infrastructure, and
policies.
6. Organization creates innovative projects in health, environment, community development
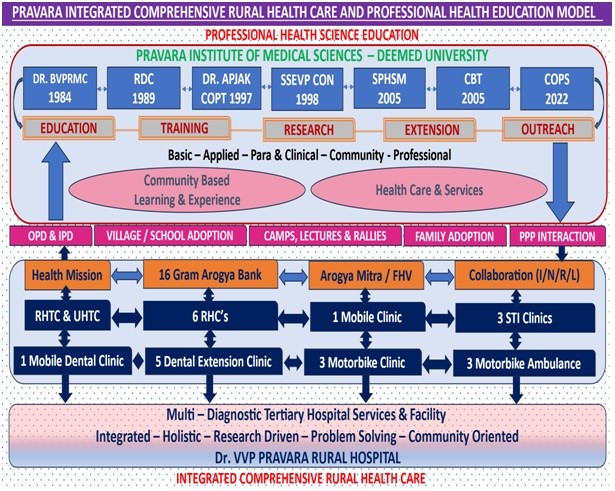
A.) Provision of Tertiary level Medical and Healthcare Services (Pravara Rural Hospital)
1. A 1275 bedded charitable, multi-disciplinary Hospital with state–of–art
gadgetsserving population of 25 lakhs covering 7 talukas of Ahmednagar district
2. Medical Hospital withOPD/IPD/ICU/OT/LatestCCL/Diagnostics/Latest
Therapeutics/Interventions/Surgical &MedicalInstrumentations/Blood
Bank/CSSD/RADIOLOGY/Anaesthesiology/CCU/CTC
3. Record number of deliveries ~ 10,000/year.
4. A650 LPM PSA type medical oxygen generationplant
5. Multi–speciality Dental Hospital with 9 departments and 318 Chairs- specialized
diagnostic, Maxillofacial,Orthognathic Surgery,aesthetic dentistry and Maxillofacial
prosthesis.
6. Rural Cancer Treatment Centre treated 3792 cases 2018 – 2023.
7. Ancillary Services such as Physiotherapy, Rehabilitation and Ayurveda, Pharmacy
and Spinal Cord Injury Centre provides healthcare.
8. Free/subsidized treatment facilitywith free food for patients and relatives
amounting to 123 crores on charity
B.) Doorstep Comprehensive Health Care Services:
1. Certificate of Appreciation for Services Rendered:
A. National Institute of Naturopathy (NIN) – Facilitation of AYUSH Drug during COVID
B. “Devdoot” Award from Indian Red Cross Society for COVID services.
C. DAPCU & DTC Ahmednagar
D. Indian Association of Physiotherapists
E. NationalIntegrated Tribal Development Project (ITDP)
F. NCC Aurangabad.
G. BAIF
H. Centre of Excellence in Tribal Health & Research by MOTA, GoI
I. Vocational Training Provider by MSSDS, GoM
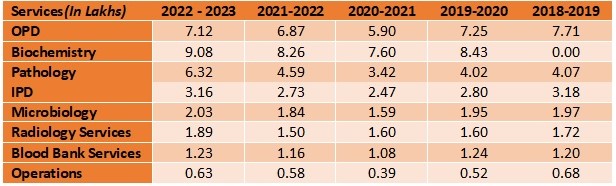
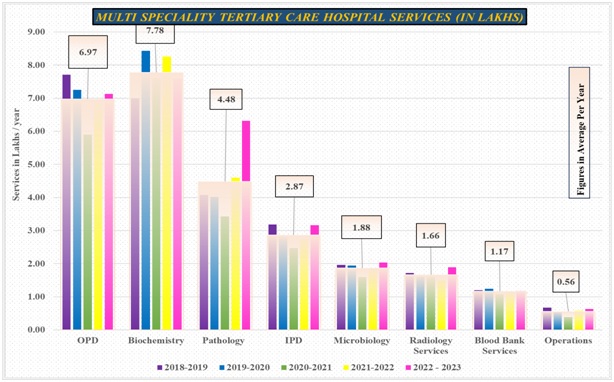
2. University Hospital serves >10.00 Lakh Patients/year for tertiary care
3. PHC Services at doorstep services to ~ 6.5 Lakh people
4. Rs. 123 crores spent on charity of patients during2018-2023
5. Collaboration with local to international level institution for research and health care
service.
6. 1200 research publication in last five years.
7. 550 qualified graduates every year contributing to nation’s workforce.
8. Consistent, Substantial increase in funding from Government and NGOs for research
9. Contributing to SDGs of 3. Good Health & Wellbeing & 4. Quality Educatio
Problems encountered and resources required:
1. To get funds from national agency to a private university.
2. Migratory labour population affecting the patient inflow and follow up.
3. Attracting specialty and super specialty consultants to a rural area.
4. Dual responsibility of clinicians between teaching, research and patient car